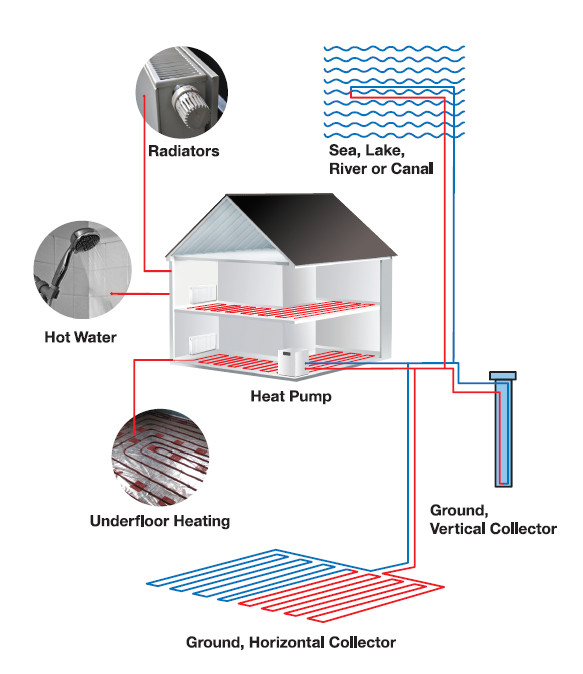
How Heat Pumps Work
Heat pumps absorb heat from the environment (the air, the ground or water) and transfer the heat into buildings – to heat the buildings without burning fossil fuels.
A heat pump works on the same principles as a domestic fridge: the heat pump in a fridge transfers heat out of the fridge and uses a heat exchanger to disperse the heat from a small radiator at the back of the fridge into the room.
An air source heat pump absorbs heat from the air – by circulating air though its heat exchanger with a fan – and transfers the heat into the building by circulating hot water though radiators, or underfloor piping circuits.
A ground source heat pump absorbs heat from the ground – by circulating water though piping in the ground – and transfers the heat into the building by circulating hot water though radiators, or underfloor piping circuits.
The heat pump increases the temperature it receives from the environment before circulating it into the house. It does this by compressing refrigerant gases. When a large volume of gas is compressed into a small space the heat energy in the gas becomes concentrated – the gas becomes very hot. The heat pump uses a heat exchanger to transfer that heat to the heating circuit in the building.
After the high pressure gas has yielded up its heat, the pressure of the gas is released and it then becomes very cold. The heat pump uses a heat exchanger to transfer that cold to the air or to a ground loop circuit. As the cold water is circulated through the ground it absorbs heat from the surrounding ground and the cycle can begin again.
How efficient is a Heat Pump?
A heat pump uses electricity to work its compressor and uses electricity to pump water through its circuits. However, most of the energy transferred into the building is transferred from the air or the ground and this energy is free. Therefore a heat pump is very efficient at providing more heat energy than it uses to perform the work needed. An air source heat pump can provide two to three kilowatts of heat for the consumption of one kilowatt of electricity. A well designed ground source heat pump installation can provide three or four kilowatts of heat for the consumption of one kilowatt of electricity.
The ratio of heat provided to electricity consumed over the heating season depends not only on the efficiency of the heat pump itself, but also the properties of the building, the heat distribution system within the building and, for a ground source heat pump, the size and efficiency of the ground loop circuit.
It also depends on the temperature available from the ground.
The temperature of the ground
The natural temperature of undisturbed ground in Britain is very close to 10°C at a depth below six metres. This is true both in summer and winter as heat moves only very slowly through the ground. However, if a ground source heat pump is absorbing heat from that ground then the temperature of the ground will fall.
The ground temperature will fall faster if a large amount of heat is being extracted from a small volume of ground. As the ground temperature falls the ground source heat pump becomes less efficient and the "Coefficient of Performance" ("CoP") may fall below the level of 4 that can be expected from a well-designed system.
The CoP of a heat pump is largely determined by the difference between the input temperature from the ground and the output temperature delivered to the building. As this gap increases the CoP of the heat pump installation falls.
How Heat Pumps Work to save money
Heat Pumps save money. Heat pumps are much cheaper to run than direct electric heating systems. GSHPs are cheaper to run than oil boilers and can be cheaper than runing gas boilers.
Because heat pumps can be fully automated they demand much less work than biomass boilers – this also saves you money.
Heat pumps save space. There are no fuel storage requirements.
Heat pumps are safe. There is no combustion involved and no emission of potentially dangerous gases. No flues are required.
Heat Pumps require less maintenance than combustion based heating systems. They also have a longer life than combustion boilers. The ground heat exchanger element of a ground source heat pump installation has a design life of 100 years.
Heat pumps save carbon emissions. Unlike burning oil, gas, LPG or biomass, a heat pump produces no carbon emissions on site (and no carbon emissions at all, if a renewable source of electricity is used to power them).
Heat pumps reduce air pollution. NO2, the largest factor in air pollution, is a by product of combustion. Heat pumps do not use combustion.
GSHPs are safe, silent, unobtrusive and out-of-sight: they require no planning permission.
Heat pumps can also provide cooling in summer, as well as heating in winter.
Installation of Heat Pumps
To get the full benefit of a heat pump installation you will need to employ someone with design and installation experience. A ground source heat pump may not perform well unless it is incorporated in a good design by someone who understands the needs of the building, the use to which the building is being put and the local geology.
For more information on installation of ground source heating from an experienced source please contact one of our members.